Inside KR
KR Decarbonization Magazine
VOL.03 | summer 2023
KR Launches New Technology Qualification Service

In April, KR established the ‘Guidelines for New Technology Qualification’ to support the efficient implementation of new technologies. The New Technical Qualification (NTQ) technical service was also fully implemented.
The NTQ process consists of four stages: feasibility and concept verification, prototype validation, system integration, and operational evaluation.
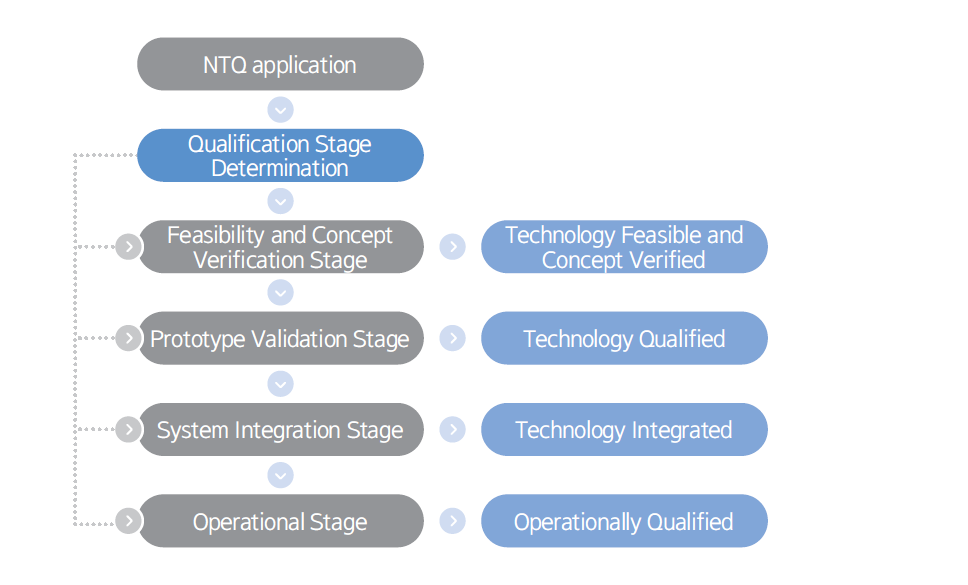
It is generally applicable to all new technologies for offshore units and marine vessels that are not normally subject to Rules, Guidance, or industry standards. The process provides a systematic and consistent evaluation of new technologies as they mature from a concept through confirmation of operational integrity in their intended application.
Through this new NTQ process, customers will be able to achieve the stability and credibility of their system at the new technology development stage. KR will actively introduce the NTQ process when working with shipbuilders and owners for the development of alternative fuel ships.
KR Awards AIP for 40Km³ LCO₂ Carrier,
Jointly Developed by DSME & SHI
With the maritime industry experiencing a growing requirement for Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) technology in response to decarbonization demands, there arises a parallel need for safe and reliable liquefied carbon dioxide carriers. These vessels play a crucial role in transporting the captured carbon dioxide to storage facilities. In the past, small vessels with a capacity of less than 3Km³ were primarily constructed for food transport. However, in recent years, there has been a notable shift in market demand towards larger carriers, driven by the need for enhanced economic efficiency. To align with this growing demand and stay abreast of technological advancements, KR has collaborated with renowned shipyards worldwide to develop liquefied carbon dioxide (LCO₂) carriers.
· SHI Designs Cover LCO₂ Characteristics and Economic Viability
KR has awarded an Approval in Principle (AIP) for a 40,000m³ LCO2 carrier developed by Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI) in collaboration with KR. The certificate was presented during a ceremony held at Nor-Shipping 2023 in Oslo, Norway.
This achievement is the result of a successful collaboration between SHI and KR, with SHI designing the cargo tank and hull structure, while KR verified the suitability of the design by reviewing classification rules and related regulations.
To maintain high pressure, the cargo tank of the LCO₂ carrier incorporates the IMO TYPE Independent-C tank. Furthermore, the vessel is constructed using materials specifically engineered to withstand low temperatures, to secure sufficient strength and durability even in environments exposed to low temperatures.
Given that LCO₂ has a higher density than LNG, more in-depth verification of structural safety for cargo holds, cargo tanks and support structures is required. The LCO₂ carrier has demonstrated reliability through structural analysis that evaluates structural strength and fatigue strength in high-stress areas.
AHN Youngkyu, Vice President of SHI said: “Our LCO₂ carrier is a good example of SHI’s advanced eco-friendly technology. We will dedicate ourselves to develop technologies to achieve carbon neutrality in the shipbuilding and maritime industry.”
YEON Kyujin, Head of KR's Plan Approval Centre, said: "This AIP is significant in that it brings us one step closer to commercializing the technology for the construction of large CCUS carriers and lays the technical foundation for the construction of larger carriers. We will continue to support CCUS-related technologies as well as decarbonization technologies."

· Structural Design of the Vessel and Conceptual Design of the Cargo Handling System by DSME, Taking into Account LCO₂ Characteristics
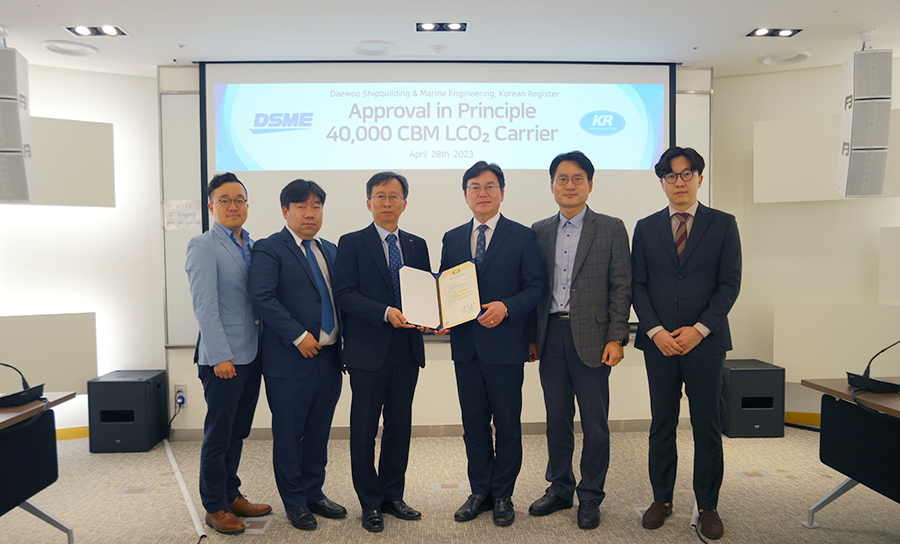
KR granted an Approval in Principle (AIP) to a 40Km³ liquefied carbon dioxide (LCO₂) carrier concept developed by Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering (DSME).
The ship that received the AIP was developed under a Joint Development Project (JDP) between KR and DSME. DSME carried out the basic and structural design of the vessel and the conceptual design of the cargo handling system. KR verified its compliance by reviewing classification rules and domestic and international regulations.
Unlike cargoes such as LNG and ammonia, which can be transported as liquids if only one of the conditions of low temperature or high pressure is met, carbon dioxide can only be transported as a liquid if both conditions of low temperature and high pressure are maintained simultaneously. At present, there are only a limited number of materials and thicknesses available for carrier tanks to maintain these conditions, making larger carbon dioxide carriers a relatively advanced technology among cargo-carrying vessels.
KIM Hyoungseog, VP & Head of DSME's Ship Basic Design Division, said: "With the completion of the conceptual design of the 40Km³, following the 12.5Km³ and 70Km³, DSME has completed its range of representative sizes of LNG carriers. This will enable us to continue to lead the market with our advanced technology in the LNG carrier sector, which has great potential for growth in the future."

Methanol-Fueled MR Tanker,
Jointly Developed by K Shipbuilding and KR Approved

KR has granted an Approval in Principle (AIP) for a methanol-fueled MR tanker, jointly developed by KR, South Korean Shipbuilders K Shipbuilding and equipment manufacturer S&SYS at Nor-Shipping 2023 in Oslo, Norway.
As part of the Joint Development Project (JDP) between the three companies, the MR tanker is designed as a dual-fuel vessel, harnessing the power of marine gas oil (MGO) and methanol. The vessel incorporates two methanol fuel tanks positioned on the port and starboard sides of the open deck
K Shipbuilding spearheaded the vessel’s basic design and the methanol fuel tank design, while S&SYS undertook the development of the fuel supply system. KR ensured the safety and regulatory compliance of the design by thoroughly reviewing national and international regulations, leading to the issuance of the AIP for the methanol-fueled MR tanker.
Methanol possesses significant advantages as a marine fuel. It is a liquid fuel similar to bunker fuel at room temperature, eliminating the need for pressurization. Compared to extreme temperature fuels like LNG, hydrogen, and ammonia, methanol is easier to store and transport. Furthermore, it is considered a green fuel with strong potential for commercialization in the maritime sector due to its technical feasibility, less toxic nature compared to ammonia, and lower technical requirements compared to LNG fuel.
KR remains committed to advancing decarbonized alternative fuel technologies, with a particular focus on providing technical support for decarbonization efforts. The ‘Methanol Fueled MR Tanker’ Joint Development Project stands as a testament to KR’s dedication to driving the industry’s transition towards greener solutions.
KR Conference 2023:
How Far Have We Come with Methanol-Powered Ships and Methanol Fuel Distribution?

In April, KR hosted the KR Conference & MacNet Strategy Seminar "How far have we come with methanol-powered ships and methanol fuel distribution?" online and offline.
Jointly organized by Maritime Cluster Networking in Korea (MacNet) and supported by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries and Busan Metropolitan City, the seminar was designed to share the status of methanol powered ship technology development and discuss the pros and cons of methanol as an alternative fuel and the sustainability of fuel supply.
Prior to the presentations, 40 experts from shipyards, shipping companies, research institutes, government organizations and maritime equipment manufacturers met to discuss preliminary issues, challenges, and ways forward for each presentation topic.
The first session consisted of three presentations on the status and prospects of methanol ship technology development, the status of shipping companies’ response to greenhouse gas regulations, and the potential of methanol as a marine fuel.
The second session included presentations on methanol alternative fuel production technology and global market trends, prospects for e-methanol and eDME production using carbon capture utilization (CCU) technology, and methanol supply chain analysis and future prospects.
Among other alternative fuels, methanol is attracting market attention not only because engines have already been developed, but also because it has several advantages, such as lower carbon emissions than LNG and easy transportation in a liquid state even at room temperature.
The seminar was an opportunity for KR customers to learn more about the sustainability of methanol-powered ships and methanol fuel supply. The presentations can be viewed on KR's official YouTube channel (www.youtube.com/TheKoreanregister).
KR Inks JDP Agreement for Fuel/GHG Emission Reduction and Verification by Autonomous Navigation
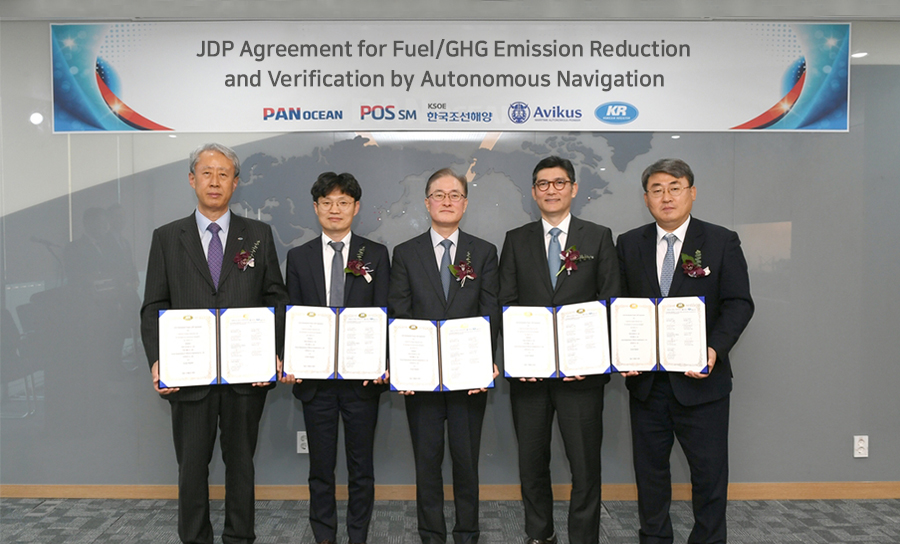

On 14 March, KR signed a Joint Development Project (JDP) agreement to verify an autonomous navigation system developed by Avikus.
Five companies, including KR, Pan Ocean, POS SM, Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering (KSOE), and Avikus, attended the signing ceremony. This JDP is significant because it will be the first time in the world that Korean shipbuilders, autonomous navigation specialists, and shipping companies will work together to verify the fuel-saving effect of using autonomous navigation systems on actual ships.
Until now, the verification of energy savings on ships, including optimal routes, has primarily relied on simulations conducted by shipbuilders or equipment manufacturers. However, this project aims to enhance reliability by verifying the results using actual ship operating data. HiNAS 2.0, the autonomous navigation system developed by Avikus to be used for this verification, was approved by KR in January this year after verifying the safety and feasibility against classification rules and international and national regulations. HiNAS 2.0 leverages augmented reality (AR) technology to empower ships in navigating optimal routes, maintaining ideal speeds, and avoiding collisions. This is achieved through the integration of data collected by artificial intelligence (AI) from sensors attached to the vessel and its sailing equipment.
KR will conduct an evaluation of the fuel savings verification framework developed in this project and verify the reliability and safety of HiNAS 2.0. Pan Ocean and POS SM will provide operational vessels and data and conduct a feasibility review of the demonstration process. KSOE will develop a fuel savings verification framework through data analysis.
Close collaboration is also expected in the future as KR undertakes technological development and demonstration work on the use of environmentally-friendly solutions. This includes pilot testing of rotor sails with Pan Ocean and certification of alternative fuel supply systems such as hydrogen, carbon dioxide and ammonia.
KR-HMM-SHI-PANASIA,
Collaborate to Conduct OCCS Field Tests

KR signed an agreement with HMM, Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI), and PANASIA to conduct integrated field tests on onboard carbon capture systems (OCCS) for ships.
KR, HMM, SHI, and PANASIA will form a joint working group to conduct a maritime field test by directly installing the domestically developed OCCS on a 2,100 TEU container ship operated by HMM within the year. The demonstration, the first of its kind in Korea, will feature a high-capacity OCCS capable of capturing and storing 24 tonnes of carbon dioxide per day in liquid form.
KR will carry out the risk assessment of the vessel, SHI and Panasia will be responsible for the design, manufacture, installation and commissioning, and HMM will operate the vessel.
The carbon dioxide captured from the container ship during the demonstration period will be delivered to shore for use in smart farms or dry ice production.
KR Joins Forces with Shipbuilding Industry
to Standardize Scope 3 Emissions

On 16 March, KR signed the first-ever Joint Development Project with Korean shipbuilders, including HD Hyundai, Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering (DSME), Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI), and the American Bureau of Shipping (ABS), to develop a method for calculating GHG Scope 3 emissions for shipbuilding.
KR and the Korean shipbuilding industry have taken a joint approach in response to market demands for disclosure of Scope 3 emissions, such as the European Union’s (EU) Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB), and the US Securities and Exchange Commission’s (SEC) Climate Disclosure Standards.
Together with HD Hyundai, DSME, SHI and ABS, KR will share, compare, and analyze each company’s Scope 3 GHG emission calculation methodology, standardize the process through consultation, and prepare international guidelines by the end of this year.
KR Successfully Co-hosts International Conference
on Wind Propulsion for Ships 2023
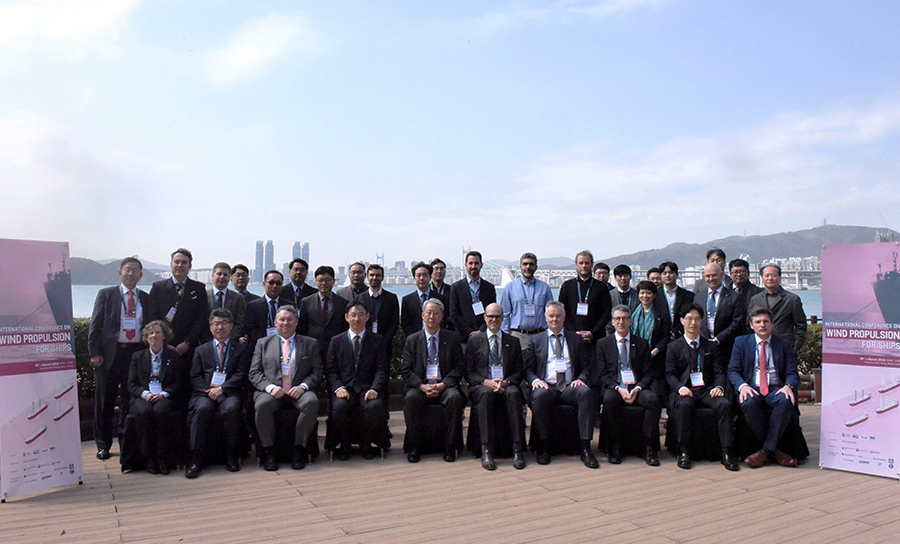

KR successfully co-hosted the International Conference on Wind Propulsion for Ships with Research Institutes of Sweden (RISE) and MacNet in Busan, Korea, in March 2023.
Key maritime leaders, including HD Hyundai, Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering (DSME), and Norsepower, the wind power specialist, gathered to share the latest trends and insights on wind propulsion technology.
At present, shipping companies are considering various measures to effectively respond to internationally tightened environmental regulations. Among them, wind propulsion technology for ships is one of the key technologies to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
KR organized this event to present the latest research and development trends in the domestic and international maritime industry on wind propulsion technology, as well as to forecast the future demand and exchange opinions with stakeholders.
At the conference, SONG Kanghyun, Head of KR Decabonization R&D Center, RYU Mincheol, Program Director at the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology (KEIT), and Sofia Werner, Lead Researcher at RISE, shared the latest information on wind propulsion technologies. Presentations were given on topics such as the status of wind propulsion technologies for responding to GHG regulations, practical verification of wind propulsion technologies, the introduction of various wind propulsion systems (rotor sails, wing sails, etc.), and the impact of wind propulsion on the maritime industry.
The presentations were followed by an open discussion session where participants exchanged views on wind power technology.
Effective collaboration among shipyards, owners, research institutes, and classification societies is crucial to effectively address the stringent regulations. KR remains committed to organizing opportunities for industry stakeholders to come together and collectively seek better solutions.