Inside KR
KR Decarbonization Magazine
VOL.05 | Winter 2023
KR GEARs Key Updates - EU ETS

KR GEARs is Set to Offer New Services from Next Year to Assist Ship Operators
in Effectively Responding to Complex Environmental Regulations.
Incorporation of Revised EU MRV Requirements
With the implementation of the EU ETS, the requirements for EU MRV have become more stringent. Now, not only CO₂ but also Methane (CH4) and Nitrous Oxide (N2O) are included in the GHG reporting scope, and emissions must be reported as CO₂ equivalent, considering the Global Warming Potential (GWP). Additionally, detailed information on emission sources and their classes must be included, along with additional fuel consumption resulting from these sources. Company-level reporting, encompassing individual ship data, has also been added. All information must be detailed in the Monitoring Plan (MP) before MRV implementation. KR GEARs will support shipping companies by providing updated MP and Emission Report (ER) templates to easily comply with the strengthened EU regulations.
VOYAGE/PERIOD Verification Service
Unlike the EU MRV, the ETS regulations involve varying settlement entities based on contractual relationships, leading to a growing demand for verified certificates for certain EU voyages. Starting next year, KR will launch a verification service that issues the statement for specific voyages or periods, separate from regular verification services. These verified voyages/periods can be automatically linked with EU MRV or IMO DCS.
Implementation of SEEMP PART III Company Audit
Since 2023, the CII regulation, based on DCS, has included company audits as an additional compliance requirement. The purpose of these audits is to ensure the effective implementation of the established SEEMP in both ships and companies, encouraging systematic management and compliance at the company level and aiming to improve the CII of international vessels. KR GEARs will support these audits by assisting with applications, managing audit reports, and scheduling.
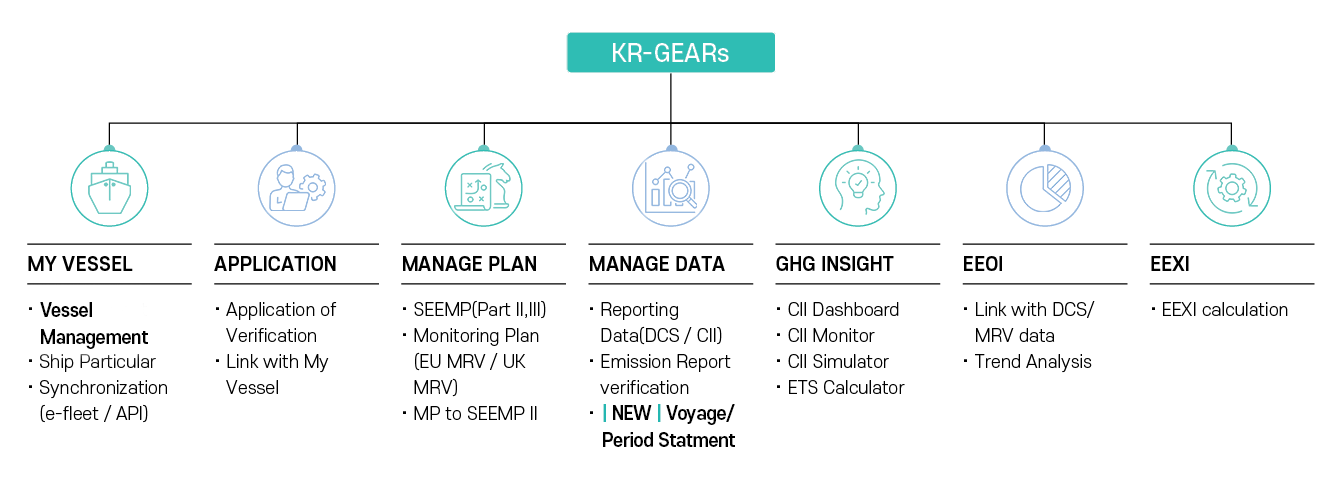
Expansion of Reporting for Biofuels and Alternative Fuels
The EU has introduced the FuelEU Maritime initiative to promote the use of renewable/low-carbon fuels. At MEPC 80, guidelines on the life cycle greenhouse gas intensity of marine fuels (LCA Guidelines) were adopted, and interim guidelines for biofuel use were approved, expanding the concept of ship fuel. Consequently, KR GEARs will update its operational information reporting template to accommodate various emission factors, enabling unrestricted reporting of fuel oil.
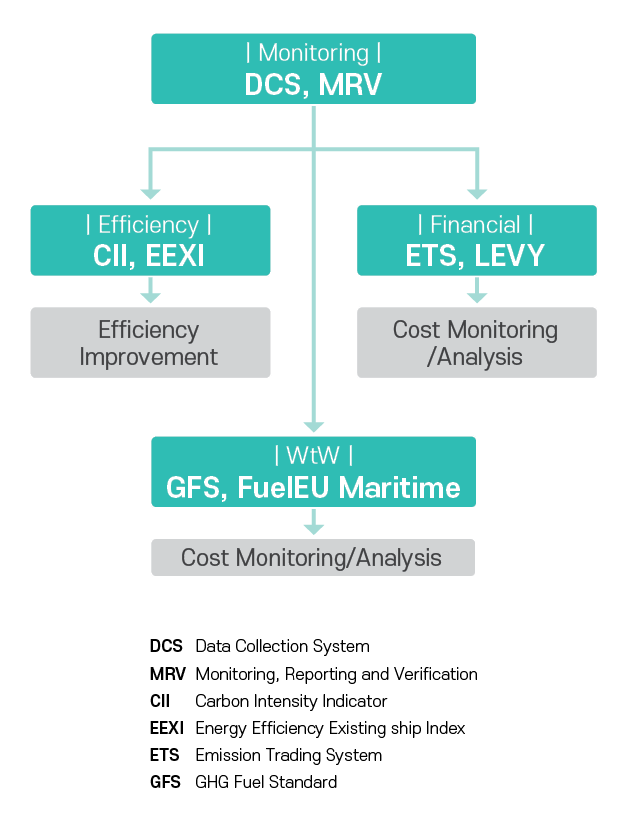
Addressing the Needs of Various Stakeholders
While shipping companies have been central to GHG regulation compliance, the introduction of the CII system and economic measures like the EU ETS has significantly increased the participation and interest of various stakeholders, including shipowners and charterers. KR GEARs has seen a rise in requests for hierarchical relationship settings aimed at sharing ship information. In response, KR GEARs plans to issue higher-level user accounts upon request, allowing a broad range of stakeholders to access user account information and utilize the service extensively.

KR awards AiP to Hanwha Ocean’s
Onboard CO₂ Capture System

Verifying technology for the absorption and mineralization of CO₂ generated onboard
KR, in collaboration with the Marshall Islands Registry, is pleased to announce the granting of an Approval in Principle (AiP) for an Onboard CO₂ Capture System (OCCS) developed by Hanwha Ocean during KORMARINE 2023 in Busan, South Korea.
With the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and the European Union (EU) strengthening regulations concerning greenhouse gas emissions, including the recent implementation of Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII) regulations earlier this year, shipping companies are faced with the imperative to closely monitor and reduce their vessels' carbon emissions to meet these stringent standards. Considering these evolving environmental regulations, onboard CO₂ capture and storage technology has emerged as a promising solution to effectively address global emissions requirements.
The onboard carbon capture and storage technology developed by Hanwha Ocean absorbs CO₂ generated on board using absorbents and converts it into mineral form. The OCCS incorporating this technology consumes very little energy compared to other CO₂ capture technologies, and the amount of additional CO₂ generated during its operation is relatively small. Furthermore, its compact design ensures efficiency in implementation.
KR verified the stability and suitability of the OCCS by reviewing classification rules and domestic and international regulations in collaboration with the Marshall Islands Registry.
YEON Kyujin, Head of KR’s Plan Approval Center, said, “Currently, the carbon capture and storage technology is expected to contribute a sizeable portion of the total global CO₂ reduction, so market demand for this technology is growing. It is meaningful for us to preemptively respond to the demand and play a major role in commercializing OCCS technology with this successful AiP.”
KANG Sang-Don, VP and Head of Hanwha Ocean’s Basic Design Department, commented, “The OCCS developed this time will be applied to 174K LNGC in the future. We will work to strengthen our competitiveness by developing eco-friendly technology that meets the ever-strengthening environmental regulations and the requirements of ship owners.”
Convergence of Digital and Carbon-neutral Technologies
Strengthened with Signing of MoU
between KR and HD Hyundai Global Service
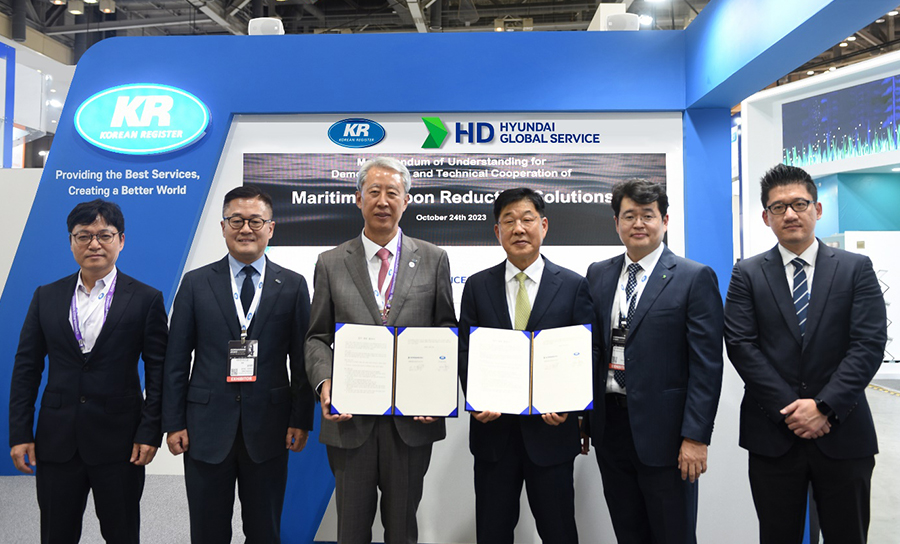

Converging Digital and Carbon-Neutral Technologies:
Active Collaboration in Big Data and AI Technology for Shipbuilding and Offshore
On 24 October, KR and HD Hyundai Global Service signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to cooperate on their verification of maritime carbon reduction solutions, at KORMARINE 2023 held in Busan, South Korea.
As decarbonization regulations are gradually being strengthened, shipping companies are actively utilizing digital technology to reduce carbon emissions more efficiently.
The two organizations signed the MoU to respond to these changes and cooperate closely for the development of “shipping and maritime big data and artificial intelligence (AI) technology”, a convergence of digital and carbon-neutral technologies.
Through this agreement, HD Hyundai Global Service plans to develop a monitoring system for carbon emissions using AI technology, forecasting and management solutions providing API (application programming interfaces), and data-related scenarios before and after applying carbon reduction solutions. KR will review the accuracy of ‘OceanWise’, the latest solution of HD Hyundai Global Service, and develop objective standards about the effectiveness of carbon reduction solutions.
LEE Hyungchul, Chairman and CEO of KR said, “In this challenging time with strengthened international decarbonization regulations, it is essential for shipping companies to find efficient ways to reduce carbon emissions to secure competitiveness, and the convergence with digital technology will be the solution. We will fully support the industry to achieve more progress in eco-beneficial digital technology through the collaboration with HD Hyundai Global Service.”
LEE Kidong, CEO of HD Hyundai Global Service added, “We are glad to be able to officially prove the value of our solution with the cooperation of KR. Our carbon footprint monitoring system will meet the various industry demands regarding carbon emission management and it will be a very useful tool for exploring new business opportunities.”
KR Publishes Research Report on Material Compatibility
for Liquid Hydrogen Storage for Ships

Joint Industry-Academia-Government Cryogenic Evaluation
Infrastructure Presentation of Evaluation Methods and Criteria
KR has announced the publication of a 'Research Report of Material Compatibility for Liquid Hydrogen Storage on Marine Application'. This report provides detailed technical information on materials suitable for on-board liquid hydrogen systems.
Following the recent resolutions at the IMO’s MEPC 80 meeting, where it was agreed upon to steer the shipping industry towards a net zero greenhouse gas emissions goal, countries are developing zero-carbon fuels and technologies for on-board use to meet their decarbonization targets.
Hydrogen stands out as one of the most promising alternative fuels. It is a carbon-free option that can also serve as a feedstock to produce alternative fuels, such as methanol. As international hydrogen transport and trade are becoming increasingly active, the demand for hydrogen carriers and hydrogen-fueled ships is expected to rise.
For safe and efficient storage and transport of hydrogen, it must be handled in its liquid state. This necessitates a cryogenic environment. However, until now, there has been a notable lack of research infrastructure and industry understanding of the materials used in marine liquid hydrogen storage systems.
To proactively respond to the future carbon-free fuel era, KR has been conducting the Korean Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries' Hydrogen Ship Safety Standard Development Project since 2020. In collaboration with Dr. Kim Yongjin's team at the Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials and Professor Kim Jeong-Hyeon's team at Pusan National University, KR has jointly established a 'Cryogenic Evaluation Infrastructure'.
The Cryogenic Evaluation Infrastructure is the only facility of its kind available in Korea. It is designed to test and analyze materials for alternative fuels that require cryogenic facilities, such as hydrogen. In this study, it was used to simulate the hydrogen environment by conducting mechanical evaluation test at -253℃, the storage temperature of liquid hydrogen.
This research report reflects the results of these tests and establishes evaluation methods for applied materials such as hydrogen pipes and tanks, as well as standards for applied materials.
KIM Daeheon, Executive Vice President of KR R&D Division, said:
"We believe that the results of this study will provide valuable guidance to industry, academia and research institutes researching and developing green ships and alternative fuels. KR will continue to support our customers and the maritime industry in various ways by developing new technologies and sharing the latest technical information to respond to environmental regulations".
The latest report is open to all interested parties and is available on KR’s website at the following link (www.krs.co.kr)
Guidelines for Using Biofuel on Ships

Following the adoption of interim guidelines for biofuel usage at MEPC 80 and the growing interest in its use on ships, KR has published technical information covering biofuel utilization.
This interim guidance remains valid until the IMO Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) Guidelines are available. Ships should follow this guidance when using and reporting on biofuels, which includes criteria for biofuel use and how it relates to the IMO Data Collection System (DCS) and the Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII).
For more information on the Biofuel Use Guidelines and other news on IMO greenhouse gas (GHG) regulations, please visit our website: (www.krs.co.kr)
KR Green Technology Conference 2023

KR Experts Deliver Insight on the Future Fuel Outlook
for Ships and Regulatory Trends
On 30 November, KR hosted the "KR Green Technology Conference 2023" in Seoul, Korea.
The global maritime industry is rapidly developing new technologies, including alternative fuels, small modular reactors (SMRs), and electric propulsion. This progress is being driven by the need to comply with increasingly stringent greenhouse gas (GHG) regulations set by organizations such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and the European Union (EU). The industry is particularly interested in applying these innovative technologies to ships.
This conference aimed to present and share the latest information on technological research achievements accumulated by KR. The goal was to facilitate responses to greenhouse gas regulations and enhance the competitiveness of green technologies by incorporating the technology needs of customers in the maritime industry. Held under the themes of "Green Ships" and "Future Fuel Technology", the conference consisted of two sessions.
The first session, titled 'Responding to IMO GHG Regulation and Green Ships,' included presentations on the current status of IMO mid-term measures and impact analysis for the shipping industry. It also covered topics such as responding to GHG regulation with IT solutions and strategies for achieving carbon neutrality through the use of alternative fuels.
The second session, "Future Fuel Technology," featured presentations on clean electric propulsion solutions to meet GHG regulations, clean fuel ship design considerations, and applications of SMRs for ship propulsion and clean fuel production.
KIM Daeheon, Executive Vice President of R&D Division, stated, "It is more important than ever to promote green ship technology and create an environment for carbon neutrality to ensure the future competitiveness of our maritime industry. I hope this conference provided an opportunity to share KR's achievements in green technology with the industry and explore future growth opportunities.”
MacNet Technical Seminar 2023 -Ⅱ
Biofuels and Ammonia: How to Overcome
Uncertainties as Alternative Fuels for Ships
A Discussion of the Production and Supply of Biofuels and Ammonia,
Engine Development Status, and Ship Demonstration
On 8 November, the Maritime Cluster Networking in Korea (MacNet) held the "MacNet Strategy Seminar-II, Biofuels and Ammonia: How to Overcome Uncertainties as Alternative Fuels for Ships".
The seminar, hosted by MacNet and supported by Busan Metropolitan City and KR, brought together experts from the government and related industries to discuss key issues. These included the production and supply of biofuels and ammonia as alternative fuels for ships to achieve the net-zero decarbonization goal for international shipping by 2050. Discussions also covered the current status of engine development, ship demonstrations, and the best solutions to achieve the net-zero goal.
The first session consisted of three presentations on the status and outlook of biofuels, international regulations, technical issues related to the use of biofuels in ships, and the use and demonstration of biofuels in ships.
The second session included presentations on the outlook for ammonia production and supply, industrial demand analysis, the status of four-stroke ammonia engine development, and the status of twostroke ammonia engine development. The third and final session was a general discussion of the topics presented in the first and second sessions.
In July this year, at the 80ᵗʰ session of the Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC), the International Maritime Organization (IMO) set a net-zero carbon target for international shipping by 2050. To achieve this goal, the shipping industry is exploring various alternative fuel options, many of which present uncertainties such as technical tradeoffs, challenges in forecasting production, supply and pricing, and bunker infrastructure issues.
Among these alternatives, biofuels were seen as having the potential to effectively reduce the carbon intensity of the existing fleet when blended with conventional fossil fuels, while ammonia was seen as a universal marine fuel capable of meeting decarbonization targets in the long term.
MacNet officials stated, "This seminar covered topics of high interest to the maritime market, such as biofuels and ammonia, and we hoped to provide practical and meaningful solutions to help the shipping industry achieve its net-zero goals.