Inside KR
KR Decarbonization Magazine
VOL.02 | SPRING 2023
New KR GEARs, Updated with Real-time CII Monitor,
CII Simulator and ETS Calculator, Enables Easier and Faster CII Rating Prediction
The newly upgraded GHG Emission Authentic Reporting system (KR GEARs) enables maritime stakeholders to more easily ensure compliance with GHG regulations in a shorter period.
Launched by KR in 2019, KR GEARs has been supporting shipping companies and operators to efficiently manage their fleet's GHG emissions data and remain compliant with tightening GHG regulations. Updated key features include a new real-time CII monitor, CII simulator, ETS calculator and advanced SEEMP Part III & CII, EU/UK MRV services.
Previous KR GEARs could calculate the CII rating based on approved DCS data. However, the new CII Monitor uses real-time operational data, allowing the CII rating to be derived and managed in real-time.
A new CII Simulator feature automatically calculates and predicts the ships’ CO₂ emissions and CII reduction effects, allowing shipping companies to manage their fleets more flexibly. Scenarios and reports are generated as each condition is selected, such as sailing speed, fuel type, operational measures and installation of energy-saving devices.
Another highlighted new feature of KR GEARs is the Emissions Trading System (ETS) Calculator. Users can predict the ETS costs by simply entering vessel information and ETS unit price. KR plans to expand the service in the near future by integrating carbon spot and futures market information into the system to easily calculate estimated ETS costs in real-time.
More information of KR GEARs can be found from its official website (https://gears.krs.co.kr) and KR website(https://www.krs.co.kr).
KR Hosts 「KR Conference 2023」
Small Modular Reactors for Ships
and Green Hydrogen Production using SMR

KR hosted the KR Conference 2023 in February to update stakeholders on the current status of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) and related technologies through expert presentations and discussions on the topic of "SMRs and Green Hydrogen Production using SMRs".
As a backdrop to the discussion on the introduction of SMRs for ships, the conference noted that the global demand for decarbonization is growing as the achievement of carbon neutrality in response to the climate crisis has emerged as a global megatrend. The value of SMRs was also highlighted as the world is spurred to strengthen its energy security in the face of global energy supply instability and deepening geopolitical crises.
Currently, major countries are promoting policies to support the development of SMRs in their respective environments, and various developers are developing their own models to ensure market competitiveness.
Korea has embarked on the development of an "innovative SMR" (i-SMR) based on its world-class nuclear supply chain and R&D capabilities. The government is focusing on continuous and strategic support and capacity building at the national level. As a result, more than 80 types of SMRs are under development worldwide. Based on the proven technology of large nuclear power plants, light water SMRs are the mainstream, while SMRs of various technologies are at different stages of development and deployment.
Offshore SMRs are essential to the establishment of greener marine energy and greener ships. The market for nuclear-powered ships in extreme environments is expected to grow as shipping lanes become more prominent in the Arctic Ocean. The market for marine SMRs related to the use of floating SMRs, such as floating power plants, hydrogen production and marine city concepts, is also expected to grow. Nuclear-powered ships have been technically proven, but an international consensus is still needed for their application to commercial vessels. This is because commercial ships pass through many countries and require a regulatory/licensing system recognized by all countries.
The offshore application of floating reactors requires mutual technical cooperation between industries led by the nuclear industry. For the design of vessels, the shipbuilding industry may take the lead, taking into account nuclear safety, and the establishment of a technical system with classification societies is required.
Considerations for offshore systems based on molten salt reactors include ensuring reactor safety in the event of an accident, maintenance, and international organizations. This is done through IEA and IMO regulations and economic and social acceptability (investment, shipping routes, ensuring social acceptability, etc.).
The Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute is promoting the Molten Salt Reactor Technology Development Project. It is reported that the Offshore Molten Salt Reactor Technology Development is expected to be completed in December 2023.
KR Publishes Ammonia Outlook Report :
Setting Course for a Zero-Carbon Marine Fuel

To provide shipowners with useful information to respond to uncertainties such as the IMO's stringent regulations and the EU's "Fit for 55" package, KR, together with Seoul National University and the Korea Institute of Energy Research, published a technical report on ammonia, one of the preferred zero-carbon fuels.
This technical document analyzes the technical characteristics, risk, mass production possibility, bunkering infrastructure, etc., of ammonia as a marine fuel. The report also performs a relative comparison with other alternative fuels through various information and assumptions that can be predicted in the current situation.
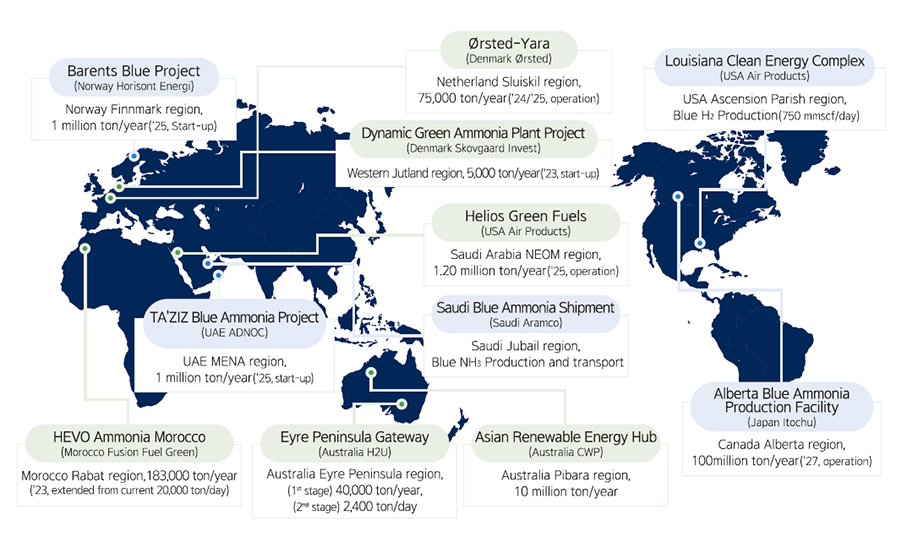
Overview of major ammonia production and transport projects worldwide
Chapter 2, Technology of Ammonia-Fueled Ships, introduces the characteristics of ammonia as a fuel, engine development trends of major engine manufacturers, ammonia fuel supply systems, attributes of tanks, and development trends related to ammonia fuel-propelled ships.
The most important milestone for the commercialization of Ammonia-Fueled Ships is the development of ammonia engines. Major engine companies such as MAN, Wartsila, WinGD, Hyundai Heavy Industries Group, and STX Engine are developing ammonia engines and are announcing plans to release them after 2024.
Chapter 3, Ammonia Production and Bunkering, presents key clean ammonia production projects, clean ammonia markets and prices, and ammonia transport and bunkering.
The figure below shows the result of forecasting the changes in the price of green and blue ammonia until 2050. Until 2030, the cost of green ammonia is unlikely to be more competitive than that of blue ammonia. However, after 2030, green and blue ammonia prices will become comparable. Therefore, the prospect of market growth and mass distribution of green ammonia are critical parameters for determining the reduction of the market price.
Projection of price changes in the future renewable ammonia market
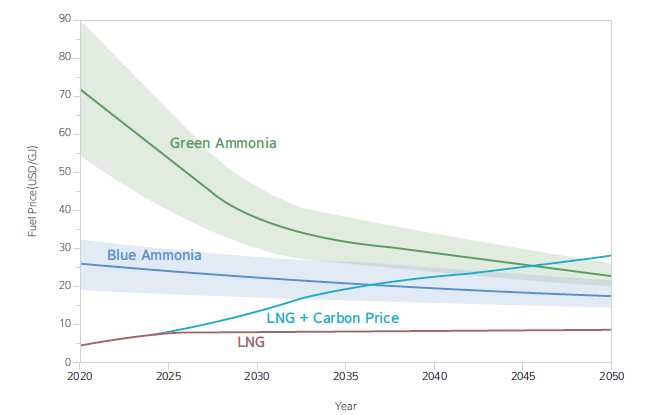
(Source: KR analysis based on data from IRENA, 2022. Innovation Outlook Renewable Ammonia)
In the case of ammonia, approximately 180 million tons (MT) of gray ammonia are produced and transported annually, indicating that the necessary port infrastructure is already well-established. There are 38 export terminals and 88 import terminals in operation worldwide, 6 of which are capable of importing and exporting. With the increase in projects involving green ammonia production and export, the number of ammonia bunkering ports is also expected to rise.
Chapter 4 introduces ammonia as a hydrogen carrier. In the maritime industry, ammonia is receiving significant attention as a ship fuel, but many countries/companies see ammonia’s importance as an efficient hydrogen carrier. Currently, fertilizer production accounts for most of the ammonia demand. However, if ammonia is used as a hydrogen carrier, the infrastructure for mass production will have to be developed. Subsequently, ammonia is highly likely to position itself as a commonly used marine fuel with reduced price and ease of supply.
The last chapter covers the next-generation marine fuel outlook. Despite the technical and economic uncertainties of ammonia as a marine fuel and uncertain carbon price due to IMO regulations, the information currently available has been gathered to predict fuel price and carbon tax and to present an analysis of the timing of the fuel transition from LNG to ammonia. The pros and cons of using bio/green methanol and ammonia were also analyzed.
The technical document can be downloaded from the KR website (http://www.krs.co.kr).
KR Approves Louis Dreyfus’ FRESH
Hydrogen Storage Vessel

KR has awarded approval in principle (AIP) to Louis Dreyfus Ports and Logistics (LDPL) for its innovative seagoing Floating Renewable Energy Solution for Hydrogen vessel (FRESH) capable of storing and supplying renewable energy in the form of hydrogen using green ammonia. The innovative vessel is expected to contribute to reducing carbon intensity in line with the global decarbonization movement.
LDPL has partnered with KR to review and approve FRESH as this novel concept is not covered by existing classification rules, to ensure that its level of safety is in line with marine industry practices. In September 2022, the partners agreed to collaborate and develop a fit for purpose technical and regulatory compliant framework ahead of the industrialization and commercialization of FRESH by 2025. On 1 November 2022, another major milestone was reached, whereby KR awarded an Approval in Principle (AiP) to LDPL, underlining the safety and technical viability of FRESH.
Mathieu Muzeau, Managing Director of the Transport and Logistics division at Louis Dreyfus Armateurs (LDA) said, “We are extremely proud to be at the forefront on the energy transition thanks to FRESH. We believe that our innovation will enable a new and global import and export supply chain centered around renewable power sources and green hydrogen and ammonia as energy carriers. Given their long-standing leadership in the field, LDA’s choice to partner with KR was obvious as we seek to bring safe and reliable vessels in the context of the accelerated decarbonization of the wider maritime industry. The AiP that LDA has secured is a demonstration of the strength of our collaboration with KR and the viability of our new vessel for future commercial use”.
Building on a decade-long collaboration with LDA, KR will continue to build on its unique technology to advance decarbonized energy logistics for both companies and provide technical support to help the maritime industry play a vital role in decarbonization efforts.
Highlighted Projects from KR’s Joint Development Work on Methanol-fueled Vessels
KR is working in close collaboration with several of the world’s leading shipyards on a Joint Development Project (JDP) with the aim of progressing methanol dual-fuel ship technology.

·AIP awarded to HHI’s methanol duel-fuel VLCC design
KR awarded Approval in Principle (AIP) to Hyundai Heavy Industry (HHI)’s methanol dual fuel 300,000 DWT crude oil carrier (VLCC).
The methanol dual-fuel VLCC, which was developed under a joint project between KR and Hyundai Heavy Industries (HHI), is powered by methanol and marine gas oil (MGO). HHI has developed the vessel so that the methanol fuel tank can be placed in either the open deck or the cargo area and KR has verified the safety and suitability of the vessel’s design, ensuring it complies with domestic and international regulations.
While verifying the vessel design with the rules, KR determined that the arrangement of the cofferdams to protect the methanol fuel tanks should be different for each of the two design variations. KR also carried out a Hazard Identification (HAZID) to determine the impact of the hazardous factors (toxicity, corrosivity, vaporization, etc.) arising from the use of methanol fuel on the crew on board, the environment and the structural strength and integrity of the vessel.
The JDP has been reviewed against the IMO Interim Guideline (MSC.1/Circ.1621) and is subject to further confirmation by the flag state.

·Collaboration with DSME on methanol-fueled 13,000 TEU container ship
Interest in methanol-fueled ships is on the rise amongst domestic and international container carriers.
KR conducted a joint study with Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering (DSME) on the structure, equipment, convention requirements and Hazard Identification (HAZID) of a methanol-fueled 13,000 TEU container ship.
This JDP was also reviewed against the IMO Interim Guideline (MSC.1/Circ.1621) and specific measures for the application of Circ.1621 were examined for various items such as copperdam arrangement, leak detection and drip tray.
The HAZID workshop with DSME provided an opportunity to identify risks for methanol-fueled container ships to be ordered in the future and to improve the technical capabilities of both companies to build optimized vessels.
KR is conducting a range of joint research projects with the world's leading shipbuilders to develop decarbonized alternative fuels such as methanol, ammonia and hydrogen, and plans to further expand technical support for decarbonization based on the methanol fuel propulsion joint development project.
KR-UPA Collaborate to Boost Methanol-Fueled Vessels

KR and Ulsan Port Authority (UPA) have signed an MOU to stimulate methanol-fueled ships and establish a low-carbon, eco-friendly energy port.
In accordance with the global decarbonization trend, methanol is in the limelight as a fuel that can significantly reduce air pollutant emissions compared to conventional ship fuel oil and can be stored and transported at room temperature. Accordingly, starting with the world’s largest shipping company Maersk’s order for a methanol-fueled container ship, Korea’s largest container shipping company HMM recently placed an order for nine methanol-fueled container ships.
The agreement between KR and UPA was made in response to the low-carbon energy transition underway in the shipping and port industries and to support the growth of domestic methanol-fueled ships and new bunkering industries.
Through this agreement, both organizations will collaborate on regulatory reform, deregulation of methanol-fueled ships and methanol bunkering, utilizing independent tank terminals in Ulsan as methanol storage facilities, testing methanol bunkering at Ulsan port and building methanol supply infrastructure in Korean ports.
Green Technology and Maritime Decarbonization Discussed at KR Seminar

"Discussion on Overcoming Challenges and Strategies for Maritime Decarbonization"
In 18 November 2022, KR hosted the KR Seminar discussing "Green Technology and Maritime Decarbonization”. This seminar has been prepared to turn the gradually increasing greenhouse gas regulation and carbon neutral trend into a new growth industry, an opportunity for development, and to work closely with the maritime sector.
The seminar consisted of two sessions and began with a keynote speech by Mr. Ryu Min-cheol, PD of the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology on ‘Overview and Prospects of Government R&D for the Development of Green Ship Technology’.
Session 1: ‘Challenges for the decarbonization of the maritime industry’
· Propulsion system conversion to meet alternative fuel and electric/hybrid regulations
· Energy efficiency improvement system for ships
· One-stop service for responding to regulations and market response: KR GEARs
Session 2: ‘Global energy transition and clean transport’
· Carbon neutral value chain: ammonia/carbon dioxide carrier
· Challenges for the shipbuilding industry: Hydrogen ships and cryogenic equipment
Each presentation was followed by a panel discussion on “Responding to IMO Regulations”, moderated by SONG Kanghyun, Head of KR Decarbonization R&D Center.
The discussion agreed that close cooperation between shipowners, shipyards, marine equipment suppliers and classification societies is essential to make the best choice among the various decarbonization measures currently under discussion.
Through the seminar, KR provided an opportunity for information exchange and fostered close cooperation among maritime partners. KR will continue to organize technical meetings to support maritime stakeholders to secure competitiveness in the latest decarbonization technologies.
